In recent years, NOVO has been the engineering design partner on several exciting and innovative development projects that include an electromechanical device, a mobile app, and a connection to the cloud. In fact, it’s becoming the exception for us to get a new project inquiry for medical device development that is not architected as a connected medical device. Gaining even more experience in this industry has been impactful for the NOVO team and that experience allows us to provide even better insight to our clients.
Definition: connected medical device
A connected medical device is a device that gathers patient data through sensor, patient, or caregiver inputs and communicates this data to servers in the cloud for the purpose of data analytics, data storage, monitoring, or machine learning.
These devices are transforming the medical industry in a big way. The advancements in connected medical devices create efficiencies for medical practitioners who can collaborate on solutions with other practitioners around the world. Additionally, a sizable volume of data can be collected on patients to be used anonymously to garner great insights into preventative care. The implications this has for patient care are far-reaching and exciting. Having the opportunity to be involved firsthand in such projects has shown us just how impactful the benefits of connected health devices can be.
CONNECTED MEDICAL DEVICE DESIGN FOR A VACCINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
 In one example, the added value represented by services managed in the cloud helped to justify the substantial investment required to develop this sophisticated system. Here’s how this project worked:
In one example, the added value represented by services managed in the cloud helped to justify the substantial investment required to develop this sophisticated system. Here’s how this project worked:
The Vaccine Management System: AccuVax
The product is a vaccine management system called AccuVax™ that NOVO developed for TruMed Systems™. This system, intended to be used at the point of care, fully automates the processes of administering vaccines to both adult and pediatric patients.
The secure cellular and WiFi network connectivity provides data to the cloud for inventory management, status monitoring, and maintenance program administration. A tablet computer used as the touchscreen user interface, automatic recordkeeping, and biometric access control make the system convenient for medical staff to use. Multiple fail-safe systems protect the valuable inventory.
The Transformation: Expanded Access to Life-Changing Vaccines
The resulting workflow automation transforms the traditionally unprofitable, error-prone, and time-consuming process of vaccine management into a profit center for small clinics, which motivates clinics to inventory a wider array of vaccines, particularly for adult patients. Drug companies, clinics, and patients benefit from ready access to critical vaccines that are recommended by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) or the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). These vaccines have been shown to reduce overall healthcare expenses by preventing a large number of more costly cases of disease. (1 – 4)
CONNECTED MEDICAL DEVICE DESIGN FOR AN INSULIN DELIVERY SYSTEM
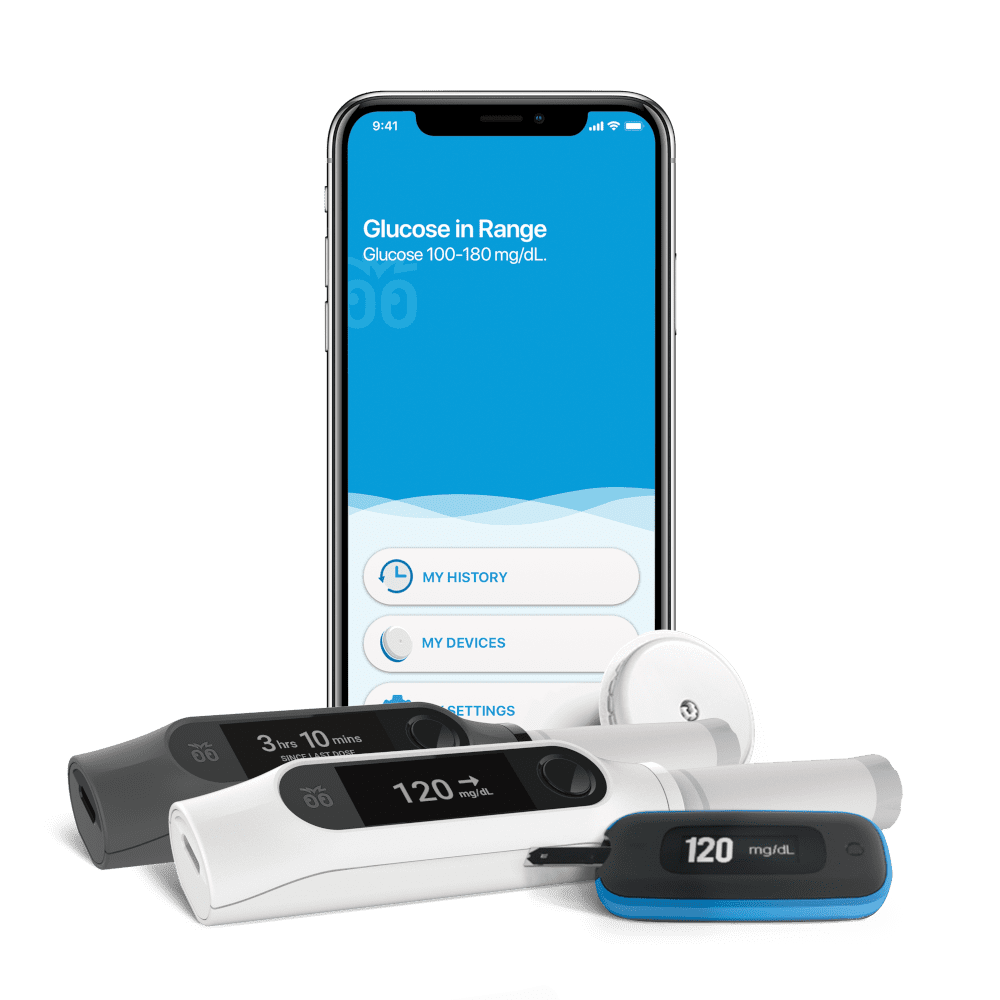
An even more compelling example of the potential for connected medical devices is a closed-loop insulin delivery system that we worked on for BigFoot Biomedical™.
Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery System: Bigfoot Biomedical
This system combines an insulin pump, a blood glucose meter (BGM), a continuous glucose monitor (CGM), a cloud-connected smartphone, and an algorithm for optimizing insulin administration. The platform is for type 1 diabetics and insulin-dependent type 2 diabetics. Managing diabetes can be challenging and exhausting. The intent of the closed-loop insulin delivery system is to alleviate much of the anxiety and wasted “mind share” for patients managing diabetes.
The Transformation: Incorporating Smartphones into Medical Devices
The cloud connection enables data analytics for continual improvement of the algorithms that control insulin delivery and serves as a remote monitoring tool for timely blood glucose information that can be accessed by physicians and other authorized recipients.
Historically, the incorporation of commercially available smartphones into medical devices was viewed as a non-starter for device companies because of the software validation issues. The FDA recognizes the potential value to patients of medical devices that incorporate mobile devices as controllers, user interfaces, or conduits to the cloud, and they are developing guidance and regulations for the medical device industry.
NOVO is excited to continue helping our partners in the medical device industry improve patient outcomes and enhance quality of care through our work designing connected medical devices. We’re also working with clients in other industries to design a variety of other products that provide additional value from being connected to the cloud. If you’re interested in partnering with NOVO on your connected medical device design and development process, reach out today.
References:
- US Government Accountability Office. Health Prevention: Cost-effective Services in Recent Peer-reviewed Health Care Literature. August 11, 2014. Available: http://www.gao.gov/assets/670/665276.pdf
- Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Vaccines Work: Key Facts and Figures. Available: https://www.jhsph.edu/ivac/resources/cost-effectiveness-of-vaccines/
- US News and World Report. Vaccines Prevent Millions of Infections, Save Billions in Costs: CDC. Available: https://health.usnews.com/health-news/articles/2014/03/03/vaccines-prevent-millions-of-infections-save-billions-in-costs-cdc
- JJ Kim. (2011, Oct. 19). The role of cost-effectiveness in US vaccination policy,” in N Engl J Med. 365:1760-1761. Available: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMp1110539#t=article
